What is LEED Certification?
LEED is a building rating system that certifies them in their different stages, the design, construction and maintenance, evaluates all kinds of buildings, and is now used worldwide.
There are other certifications of sustainability for buildings and the main objective of all is to reduce the environmental impact generated by the building, what makes a leader to the LEED certification is that it is the only certification at the international level, which gives it a great value.
This certification consists of a system of points where we evaluate the ecological strategies grouped into categories depending on the final score will certify the building.
Benefits of LEED Certification
The buildings that come with this certification have increased exponentially in recent years.
Because, in addition to prestige, consider your building as a sustainable, LEED Certification provides other advantages:
- Increase the value of the building, on the market.
- Reduction of operating expenses.
- Increases the marketing for the promotion of the building.
- Improving the productivity of the people that occupy the building.
Who created it and who gives the LEED Certification?
The concern with sustainable spaces and energy-efficient arises at the beginning of the century to the root of the greenhouse effect. In this situation the United States Green Building Council (USGBC) began to work in sustainability strategies aimed to reduce the overall environmental impact of the building in 1998 was named a LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design).
The only institution with the authority to grant to the LEED certification is the Green Building Certification Inc. (GBCI). The aim of the USGBC to create LEED is that you can create a healthier and more sustainable future
Background LEED
1993 it was founded on the USGBC with David Gottfried as president, Mike Italian as Chief Executive officer and Rick Fedrizzi as its founding president.
1998 arises LEED version v1.0 and 19 projects initiated the process of certification.
2001 and based on the learning of the version 1.0 launched LEED 2.0 which implemented more sectors may get the Certification you READ.
2003 and with significant numbers launched LEED v2.1 with the what in a year were able to certify 100 projects, among which were sectors such as:
- Existing buildings
- Commercial Interiors
- Core & Shell
In 2009, with quite a bit of experience reflected in the new version LEED v2009 were introduced credits based on scientific studies that avalaran the rigorous evaluation LEED, to this date had already been certified 5000 projects worldwide.
In 2015, there arises version LEED v4 with a better approach and emphasis on the materials and resources to continue to increase the number of certified projects.
And finally, in 2019, there arises version today, current LEED v4.1
LEED v4.1
LEED is continuously evolving, now the current version is LEED v4.1 some of the features of this version are:
- Ensure that everyone involved in any phase of the building sustainable benefit from the design.
- The benefit granted by the green building both short-and long-term.
- To ensure a greater quality by integrating innovative designs, technologies and the strict selection of materials for their construction.
- To reduce the operating costs of the building sustainable.
The intent of LEED to a newer version of the certification is that a greater number of projects are able to reach it, without losing the requirement of each point, but impulsandonos to have best practices and strengthen our commitment in the project on the planet.
Systems LEED
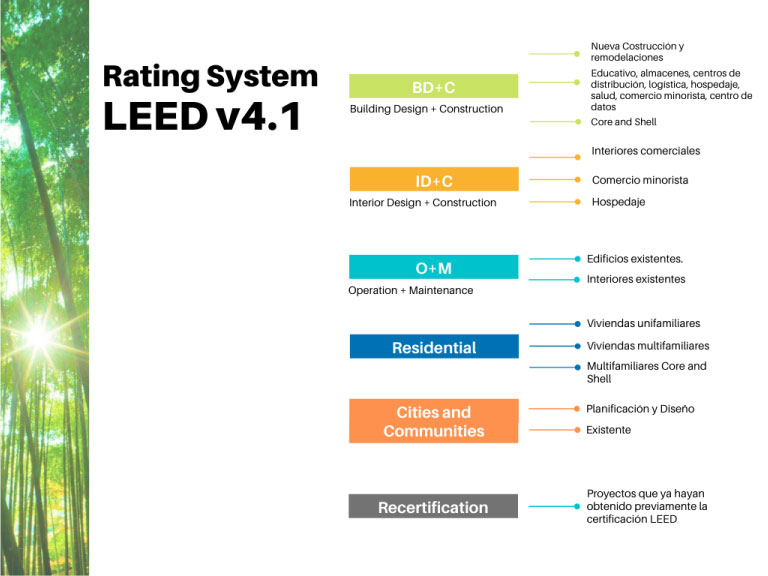
The certification is very versatile because they developed different types of standards depending on the type of project and the phase in of the building.
The LEED rating system is:
- BD+C Building Design and Construction
- ID+C Interior Design and Construction
- O+M Operations + Maintenance
- Residential
- Cities and Communities
- Recertification
Evaluation categories for LEED Certification
There are 9 categories, and each one gives to specific points in order for the project to be certified.
- Integrated process of Design and Construction.
- Sustainable Sites
- Water efficiency
- Energy and Atmosphere
- Materials and Resources
- Quality of Indoor Environment
- Location and Transport
- Innovation
- Regional Priority

Levels of LEED certification
Projects seeking LEED certification earn points across the categories of evaluation, depending on the amount of points achieved by the project obtains one of the four levels of LEED Certification:
- Certified: 40 to 49 points
- Silver: 50 to 59 points
- Gold: 60 to 79 points
- Platinum: 80 to 110 points

To obtain the LEED certification for your project is an international symbol of excellence in sustainability, which means that the building is:
- Reducing carbon emissions
- Conserving natural resources
- Reducing operating costs
- Prioritizing sustainable practices
- Creating a healthier environment
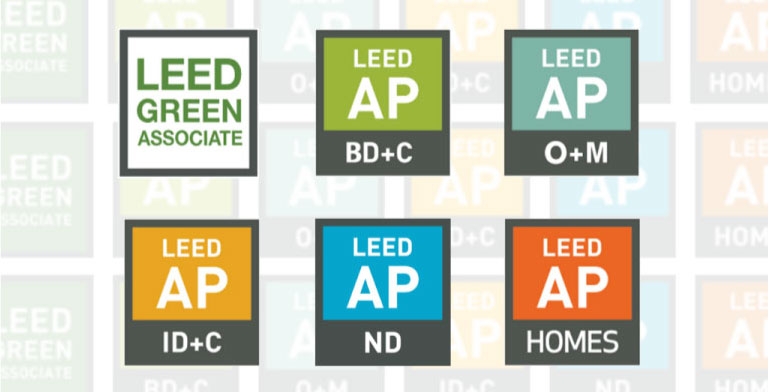
Types of credentials LEED
There are 2 types of credentials: LEED Green Associate (GA), and LEED Accredited Professional (AP).
LEED Green Associate (GA): This card indicates that you have the general knowledge of the practices of sustainable construction and sustainable.
LEED Acredited Professional (AP): This credential indicates that apart from the general knowledge of the practices of sustainable construction and sustainable, also have knowledge of one of the LEED rating systems specific, in order to obtain this credential, you must submit the examination of general knowledge and specialty.
In both cases, you must have a continuing education after obtaining your credential.